What is the Marburg virus and how dangerous is it?
The highly-infectious disease is similar to Ebola, with symptoms including fever, muscle pains, diarrhoea, vomiting and, in some cases, death through extreme blood loss.
Hundreds of people have died from the virus in recent years, almost all in Africa.
What is the Marburg virus and how dangerous is it?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), on average, the Marburg virus kills half of the people it infects, with previous outbreaks killing between 24% and 88% of patients.
The virus was first identified in 1967 after 31 people were infected and seven died in simultaneous outbreaks in Marburg and Frankfurt in Germany, and Belgrade in Serbia.
The outbreak was traced to African green monkeys imported from Uganda.
But the virus has since been linked to other animals.
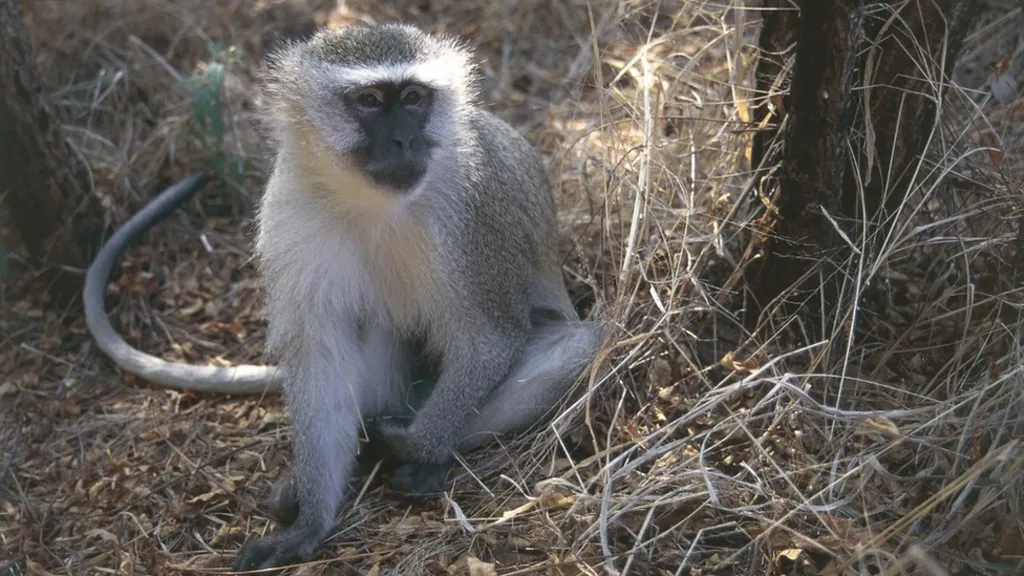 The Marburg virus was first traced to the African green monkey
The Marburg virus was first traced to the African green monkey
Among humans, it is spread mostly by people who have spent long periods in caves and mines populated by bats.
In recent years, there have also been outbreaks of the Marburg virus in:
- Equatorial Guinea
- Ghana
- the Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Kenya
- South Africa
- Uganda
- Zimbabwe
A 2005 outbreak in Angola killed more than 300 people.
However, in the rest of the world, only two people have died from the Marburg virus in the past 40 years - one person in Europe and one in the US.
Both had been on expeditions to caves in Uganda.
Where have most cases been recorded?
Five people have died in Tanzania's north-western Kagera region. Three other people are being treated in hospital and authorities are tracing 161 contacts.
This follows an outbreak in Equatorial Guinea in February, which is known to have infected nine people and killed seven.
The WHO is investigating 20 more probable cases there.
Other major outbreaks include:
- 2022, Ghana: three cases, two deaths
- 2017, Uganda: three cases, three deaths
- 2012, Uganda: 15 cases, four deaths
- 2005, Angola: 374 cases, 329 deaths
- 1998-2000, DR Congo: 154 cases, 128 deaths
- 1967, Germany/Serbia: 31 cases, seven deaths
What are the symptoms of the Marburg virus?
The virus begins abruptly with:
- a fever
- severe headache
- muscle pains
This is often followed, three days later, by:
- watery diarrhoea
- stomach pain
- nausea
- vomiting
According to the WHO, "the appearance of patients at this phase has been described as showing 'ghost-like' drawn features, deep-set eyes, expressionless faces and extreme lethargy."
Many people go on to bleed from various parts of the body, and some die eight to nine days after first falling ill, because of extreme loss of blood and shock.
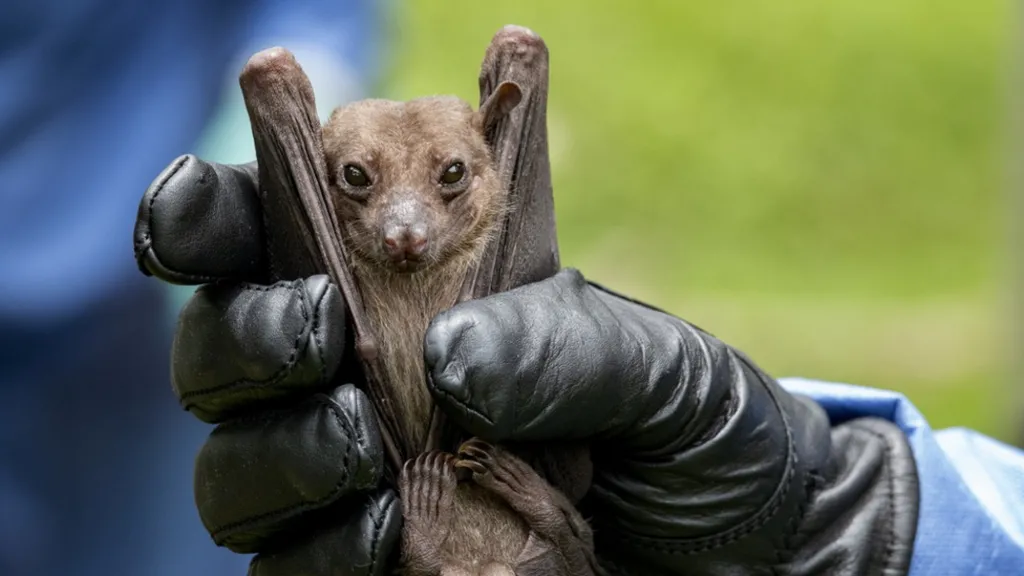

The Egyptian rousette fruit bat is one of the main carriers of the virus
How is the Marburg virus spread?
African green monkeys and pigs can carry it.
The Egyptian rousette fruit bat often also harbours the virus.
Among humans, it spreads through bodily fluids and contact with contaminated bedding.
Even after people have recovered, their blood or semen can remain infectious for many months afterwards.
How can it be treated?
There are no specific treatments or a vaccine for the virus.
But a range of blood products, drug and immune therapies are being developed, the WHO says.
Doctors may be able to alleviate the symptoms by giving hospital patients plenty of fluids and using transfusions to replace lost blood.
How can it be contained?
People in Africa should avoid eating or handling bushmeat, according to Gavi, an international health organisation.
People should also avoid contact with pigs in areas with an outbreak, says the WHO.
Men who have had the virus should use condoms for a year after the onset of symptoms or until their semen tests negative for the virus twice.
Those who bury people who have died from the virus should also avoid touching the body.
*This article was first publised by the BBC on 23 March 2023.
Source: BBC