RED ALERT: Global Alarm over Ultra-Deadly Monkeypox strain Crossing Borders
HEALTH chiefs are poised to declare an international public health emergency as an ultra-deadly strain of mpox that can spread by touch starts to cross borders.
The strain has been discovered in two new countries in recent weeks after cases have been surging in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) for months.

Health cheifs are considering declaring a second global health emergency
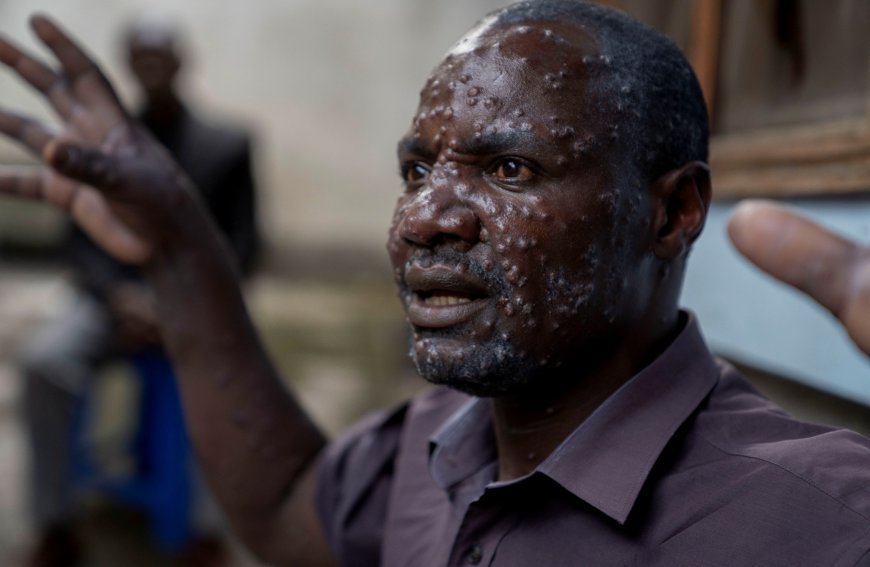

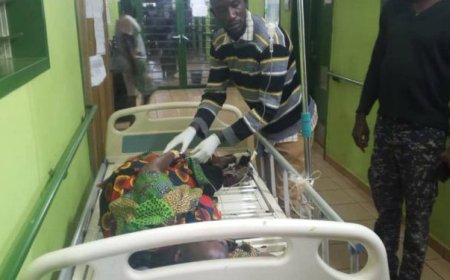
Jean Kakuru Biyambo, 48, a father being treated for mpox at the Goma general hospitalCredit: Reuters
Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, from the World Health Organisation (WHO), wrote on X on Wednesday that experts are worried the mutant bug has "potential for further international spread within and outside of Africa."
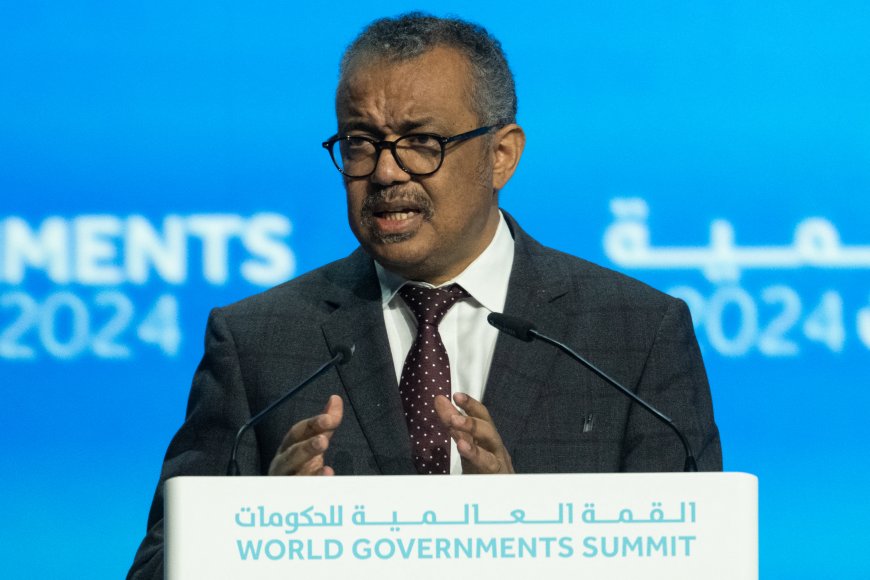

Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, from the WHO, fears international spread of the more deadly strain of mpoxCredit: AFP
He added: “I am considering convening an International Health Regulations emergency committee to advise me on whether the outbreak of mpox should be declared a public health emergency of international concern."
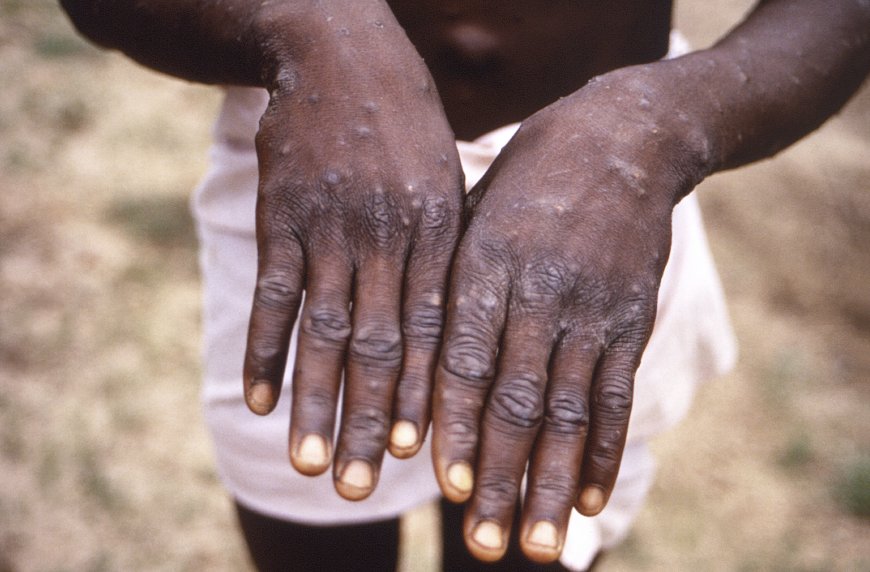
Mpox is a viral infection that causes flu-like symptoms and pus-filled lesions.
And until a few years ago most cases of it were reported in central and west Africa.
But in 2022, the WHO declared a public health emergency, when a strain of mpox called clade 2 triggered the global outbreak that reached over 100 countries - including the UK.
The DRC has been battling with it's own variant, called “clade 1a” for decades.
This version is more deadly, with a fatality rate of around five per cent in adults and 10 per cent in children, compared to three per cent for its predecessor.
In April, alarm bells were raised when scientists found a new easier-to-catch strain of mpox with “pandemic potential” in Kamituga, a small mining town in the DRC.
The new bug, dubbed “clade 1b” is behind a recent surge in cases in the east of the country.
The DRC has reported over 29,000 cases and 1,100 fatalities – the vast majority of them children – since the beginning of 2023.
Kenya late last month registered a single case of clade 1b mpox.
And, at the weekend, Uganda announced its first two cases had been detected.
Vaccines and treatments were previously used to combat the global outbreak, but they are not available in many countries, including Congo.
Earlier this month, authorities said it had reached the major city of Goma, which has an international airport that operates frequent direct flights to and from Europe.
"Pathogens don’t recognise borders," Ben Oppenheim, a global health experts and senior director of US company Ginkgo Biosecurity, previously told the Sun.
"Goma is an important regional transit point, which heightens the risk of the virus spreading regionally and potentially globally – including to Europe and the UK," he said.
Trudie Lang, professor of global health research at Oxford University, added: "It is quite possible people with the infection and who are infectious could get on a flight and transmit this elsewhere".
The mpox symptoms that have nothing to do with spots
The most obvious mpox symptom is the hallmark spots.
According to the NHS, these lesions go through four stages, from flat spots to raised spots, to blisters to scabs.But people are also likely to experience flu-like symptoms, which will begin between five and 21 days after infection.The symptoms often get better by themselves over two to four weeks.The NHS says these include;
- Inflammation of the rectum (proctitis) – for example, pain or bleeding from your back passage
- High temperature (fever)
- Headache
- Flu-like symptoms, including muscle and back aches, shivering and tiredness
- Swollen glands that feel like new lumps (in the neck, armpits or groin)
If you have some of these symptoms and believe you could have monkeypox, you should stay at home, avoid close contact with others and get medical help by phone until you’re assessed.
There are some complications associated with mpox, such as bacterial infection from skin lesions, mpox affecting the brain (encephalitis), heart (myocarditis) or lungs (pneumonia).
Mpox in the UK
Government data has shown 3,553 cases of mpox were recorded in the UK in 2022.
The Department for Health has said: “The outbreak has mainly been in gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men without documented history of travel to endemic countries.”
But cases have fallen sharply in the past six months as a result of vaccination and testing.
At the time of writing, only 20 cases have been recorded in the UK in 2023.
Source: The Sun